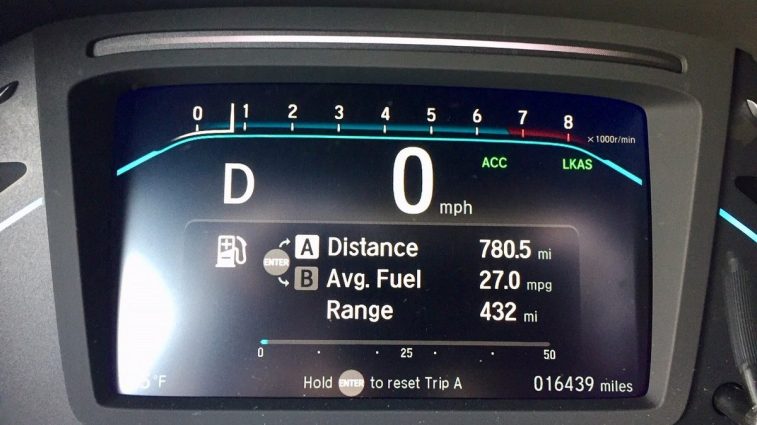
Miles per gallon (mpg) is a calculation of a motor vehicle’s fuel economy. The simple formula is miles traveled divided by gallons of fuel consumed.
Mpg is the chief fuel economy measurement for motor vehicles and the basis for ratings by the Environment Protection Agency (EPA). Manufacturers test their vehicles, usually pre-production examples, under controlled laboratory conditions and report city, highway, and combined mpg. The EPA reviews the results and retests 15% to 20% of the vehicles in its facility to confirm.
Since 2011, new passenger vehicles, such as SUVs and passenger vans with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of 10,000 pounds or more, pickup trucks with a GVWR over 8,500 pounds and a bed length over 72 inches, and cargo vans with a GVWR over 8,500 pounds are exempt from EPA fuel economy testing requirements. So are motorcycles.
Gasoline-powered, hybrid gasoline-electric, and diesel-powered vehicles all carry mpg ratings. Plug-in hybrids and battery-electric vehicles use a related rating, miles per gallon equivalent (mpge).
EPA fuel economy ratings are reported on the new vehicle information window sticker known as a “Monroney.” Current and historical mpg ratings for all makes and models sold in the United States are searchable at the EPA’s FuelEconomy.gov website.